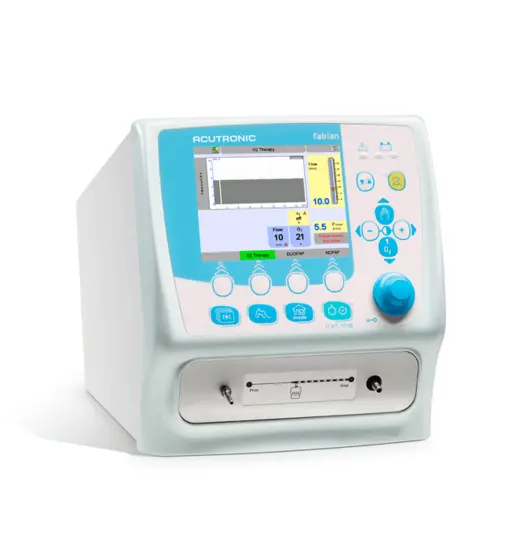
fabian HFO Beatmungsgerät

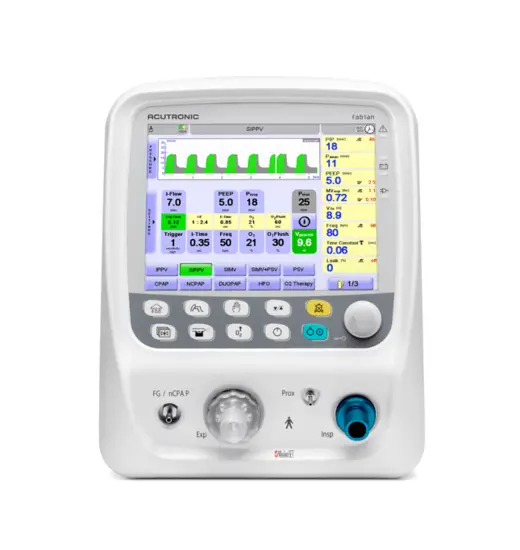
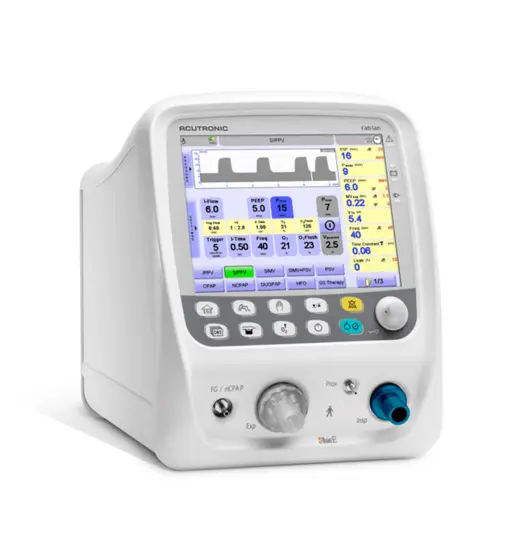



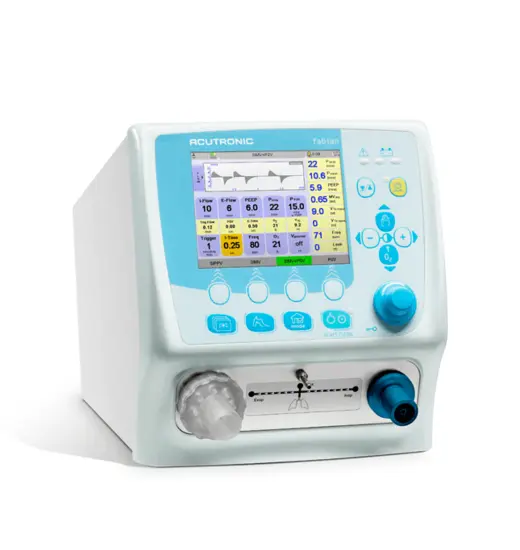
fabian HFO Beatmungsgerät
Das mit einem 10,4-Zoll-Touchscreen ausgestattete fabian HFO ist unser leistungsstärkstes Beatmungsgerät. Dieses Modell verfügt zusätzlich zu all seinen modernen nichtinvasiven und konventionellen Beatmungsmodi über eine echte Einmembran-Hochfrequenzoszillation mit aktiver Inspiration und Exspiration. Zudem wurde das Gerät mit Forcierter Oszillationstechnik (FOT) erweitert, einem präzisen und intelligenten Lung Recruitment Tool.* Fabian ermöglicht es dem Kliniker, das höchste Versorgungsniveau beizubehalten, wenn sich der Zustand und die Bedürfnisse des Säuglings ändern.
*FOT ist möglicherweise nicht in allen Regionen erhältlich. Wenden Sie sich diesbezüglich an Ihren Vyaire-Vertreter vor Ort.
Beachten Sie bitte, dass möglicherweise nicht alle Produkte, Dienste oder Produktmerkmale und Dienstleistungen in Ihrer Region erhältlich sind. Wenden Sie sich diesbezüglich an Ihren Vyaire-Vertreter vor Ort. Die Informationen auf dieser Seite sind für Fachkräfte im Gesundheitswesen vorgesehen.
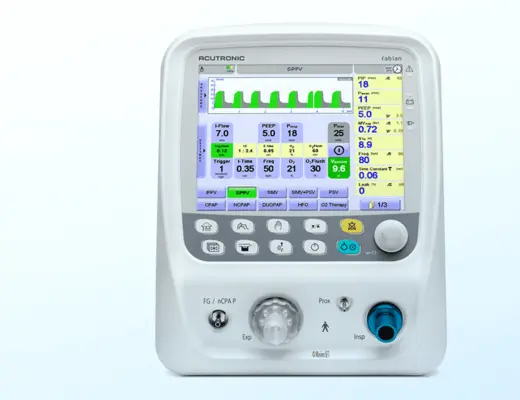
Das fabian HFO erfordert zur Verbindung des HFO-Moduls mit dem Beatmungssystem keine zusätzlichen Schlauchsets, was die folgenden Vorteile bietet:
- Es wird mehr Leistung vom internen HFO-Modul an den Patienten abgegeben
- Alle Beatmungsmodi (konventionelle Beatmung und HFOV) können mit demselben Beatmungssystem verwendet werden, was einen nahtlosen Übergang zwischen den beiden Modi ermöglicht
- Reduzierte Behandlungskosten und
- Effizienteres Zeitmanagement für Pflegekräfte.

- Alle diese Funktionen und sogar noch mehr in nur einem Gerät: Alle konventionellen Beatmungsmodi für Neugeborene und Kinder (einschließlich Volumengarantie), nichtinvasive Beatmungsmodi (NIV), O2-Therapie mit High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) und einzigartiger Hochfrequenzoszillation (HFO) mit Lungenrekrutierungsmanöver und Volumengarantie.
- Beatmungsmodi für Neugeborene und Kinder (IPPV, SIPPV, SIMV, SIMV+PSV und PSV) mit unabhängig einstellbarem Inspirations- und Exspirationsflow reduzieren die Atemarbeit und unbeabsichtigten PEEP.
The challenge of optimal lung recruitment
FOT – Forced Oscillation Technique
The patented Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT) is a non-invasive, protective and easy method that allows the clinician to assess an optimally recruited lung at the bedside. Strategies for optimizing lung volume are critical – especially in preterm newborns. Usually, CPAP, PEEP and MAP are adjusted according to oxygenation, both in conventional modes and during High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV). But oxygen saturation (SpO₂ or pO₂) may be an imperfect guide for MAP or PEEP titration: there remains a risk that PEEP-induced over-distension and intra-tidal recruitment/derecruitment go unnoticed.
An exclusive, patented option for the fabian:
FOT by setting the optimal CPAP, PEEP and MAP level for the individual patient, greatly reduces mechanical stress to the lungs, and brings down ventilation costs.
Direct feedback from the lung:
FOT allows the clinicians to assess the optimal mean airway pressure by measuring respiratory system reactance Xrs, and tailors protective HFOV or CMV ventilation support to the individual patient.